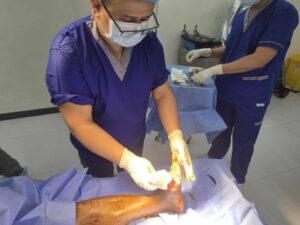
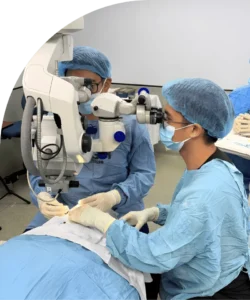
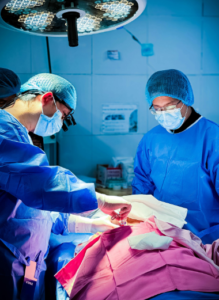
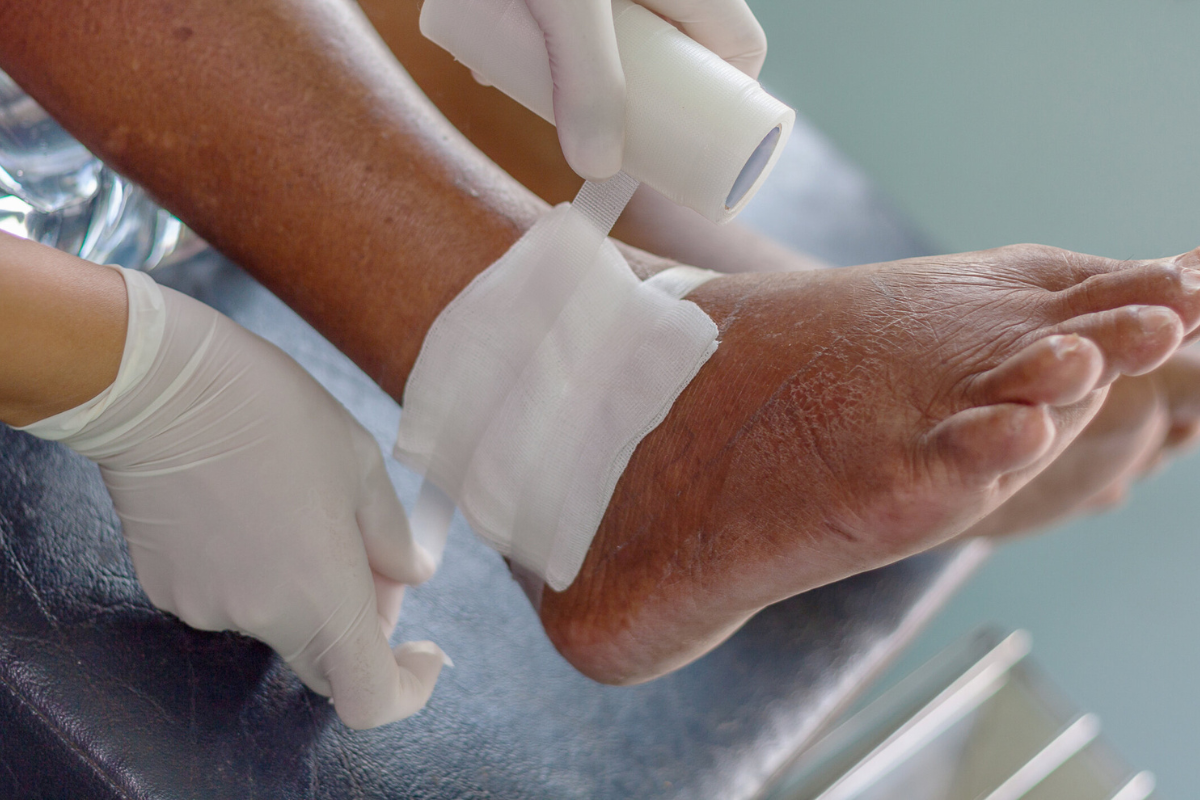
Non-healing wounds can be a significant source of discomfort, limited mobility, and prolonged medical concern for many patients. These wounds, often persistent beyond typical healing timelines, arise from various causes such as diabetes, vascular insufficiencies, infections, trauma, or pressure ulcers. In orthopedic contexts, non-healing wounds may indicate underlying issues like bone involvement, soft tissue compromise, or poor circulation, which require specialized intervention. Without timely and effective treatment, these wounds can lead to complications including chronic pain, infections, and even systemic health issues. Understanding the unique challenges associated with non-healing wounds is essential for both patients and healthcare providers to navigate appropriate treatment pathways. Orthopedic specialists play a pivotal role in evaluating the severity of wounds and designing treatment plans that address both tissue repair and underlying orthopedic conditions. The integration of advanced diagnostics, specialized wound care, and surgical interventions can significantly improve recovery outcomes.
Understanding Non-Healing Wounds
Non-healing wounds are characterized by a failure to progress through the standard phases of healing, including inflammation, tissue formation, and remodeling. These wounds often linger for weeks or months, showing minimal improvement despite conventional care. Common causes include diabetes-related neuropathy, peripheral vascular disease, prolonged pressure, or post-surgical complications. Trauma or fractures that compromise local blood supply can also result in persistent wounds. Patients may notice symptoms such as persistent redness, swelling, pain, or discharge, signaling that the healing process is impaired. Early recognition and assessment of non-healing wounds are crucial, as delays in treatment can lead to infection, tissue necrosis, or chronic disability. For orthopedic patients, wounds may reflect deeper skeletal or soft tissue involvement, requiring a combination of surgical and non-surgical interventions. Proper wound assessment, including measuring size, depth, and tissue quality, helps guide the appropriate orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds.
Why Orthopedic Intervention Is Crucial
Orthopedic intervention is essential when wounds are associated with bone or joint complications. Specialists assess not only the wound itself but also underlying structural issues that may impede healing. Imaging techniques such as X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans are often utilized to detect hidden fractures, bone infections, or abnormal tissue formations. Unlike standard wound care, orthopedic treatment addresses the mechanical and structural aspects that may prevent proper healing. This might include stabilizing a fracture, removing necrotic tissue, or ensuring proper alignment to reduce pressure on the affected area. Additionally, orthopedic teams collaborate with wound care specialists, physical therapists, and nutritionists to develop comprehensive treatment plans. Proper intervention helps minimize long-term disability, reduces the risk of infection, and promotes more efficient wound closure. For patients with complex or persistent wounds, timely orthopedic care can be the difference between prolonged suffering and successful recovery.
Common Orthopedic Treatments for Non-Healing Wounds
Orthopedic treatments for non-healing wounds vary depending on the severity, location, and underlying cause. Surgical debridement is often employed to remove dead or infected tissue, creating a healthier wound environment that encourages natural healing. In cases involving fractures or bone exposure, stabilization techniques such as external fixation or internal implants may be necessary. Bone grafts or tissue grafts can also support healing by providing structural reinforcement and promoting tissue regeneration. Orthopedic surgeons may combine these techniques with advanced dressing methods or negative pressure therapy to enhance outcomes. Ensuring that wounds are free from infection is critical, as bacterial colonization can delay healing and compromise orthopedic interventions. Patients often require close monitoring to track progress and adjust treatments as necessary. By addressing both tissue and structural components, orthopedic treatments for non-healing wounds aim to restore function while minimizing complications.
Advanced Therapies in Orthopedic Wound Management
Modern orthopedic wound care incorporates advanced therapies to accelerate healing and improve patient outcomes. Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT), for instance, uses controlled suction to remove excess fluid, reduce swelling, and promote tissue growth. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) exposes the patient to high-pressure oxygen, enhancing blood flow and stimulating tissue regeneration. Growth factor treatments and stem cell therapies are increasingly utilized to support cellular repair and accelerate wound closure. These advanced approaches are often combined with surgical interventions for comprehensive care. Orthopedic specialists select therapies based on wound characteristics, patient health status, and healing potential. The integration of these innovative treatments represents a significant advancement in managing complex, non-healing wounds. Patients receiving these therapies often experience improved healing rates, reduced pain, and a lower risk of recurrent wound complications.
The Role of Infection Control in Healing
Infection control is a cornerstone of effective orthopedic wound management. Non-healing wounds are particularly vulnerable to bacterial colonization, which can compromise tissue repair and increase the risk of systemic infection. Orthopedic specialists employ strategies such as targeted antibiotics, antimicrobial dressings, and regular wound monitoring to manage infections. Identifying pathogens through laboratory cultures allows for personalized treatment and reduces the likelihood of antibiotic resistance. Maintaining strict hygiene and sterile procedures during wound care further prevents contamination. Prompt infection control not only facilitates faster healing but also protects bone and joint structures that may be involved. Patients are advised to follow post-treatment care instructions carefully to prevent secondary infections and ensure long-term wound stability.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation plays a critical role in recovery from non-healing orthopedic wounds. Maintaining mobility and avoiding prolonged pressure on affected areas are essential for promoting circulation and tissue repair. Physical therapists design individualized programs to strengthen muscles, improve range of motion, and reduce the risk of secondary injuries. Weight management and posture adjustments may be recommended to relieve pressure and optimize wound healing. Rehabilitation also includes strategies to prevent pressure ulcers and recurring wounds, especially for patients with limited mobility or chronic conditions. Coordinating therapy with orthopedic treatment ensures that mechanical stress on healing tissues is minimized. Gradual, supervised activity helps patients regain independence while supporting tissue regeneration. By integrating physical therapy with orthopedic care, patients achieve better functional outcomes and reduced complication rates.
Patient Lifestyle Adjustments for Faster Healing
Lifestyle factors significantly influence the healing of orthopedic wounds. Nutrition is particularly important, as protein, vitamins, and minerals support tissue repair and immune function. Proper hydration aids in circulation and the delivery of nutrients to damaged areas. Diabetic patients must carefully manage blood sugar levels to prevent delayed healing. Smoking cessation is highly recommended, as tobacco use impairs circulation and tissue repair. Patients may also benefit from weight management to reduce pressure on lower extremities or affected joints. Stress reduction and adequate sleep further contribute to overall healing. Making these adjustments in conjunction with medical care enhances recovery, reduces complications, and supports long-term wound health.
Monitoring and Long-Term Care
Consistent monitoring is vital for patients with non-healing wounds to ensure that treatment remains effective. Regular follow-ups allow orthopedic specialists to track progress, detect complications early, and adjust therapies as needed. Wounds involving bones or joints require particularly careful observation due to the risk of deep infections or structural instability. Coordination among orthopedic surgeons, wound care specialists, and primary care providers ensures a comprehensive approach to recovery. Long-term care may involve periodic imaging, laboratory testing, and lifestyle counseling to maintain healing and prevent recurrence. Patients are encouraged to actively participate in monitoring, report any changes, and adhere to care plans. Effective long-term management enhances quality of life and reduces the likelihood of future orthopedic complications.
FAQ
How long does it typically take for orthopedic wounds to heal?
Healing timelines vary based on wound size, depth, infection status, and patient health. Some wounds may heal within weeks, while others may require several months of treatment and rehabilitation.
Can non-healing wounds be prevented with early orthopedic care?
Early orthopedic assessment and intervention can significantly reduce the risk of non-healing wounds, especially in patients with fractures, diabetes, or vascular issues.
What are the signs that a wound needs urgent orthopedic attention?
Signs include persistent pain, swelling, redness, discharge, foul odor, or lack of healing progress despite standard care. These symptoms indicate the need for immediate evaluation.
Are there non-surgical options for treating non-healing orthopedic wounds?
Yes, options include negative pressure therapy, hyperbaric oxygen therapy, growth factor applications, and advanced dressing techniques, though some cases may still require surgical intervention.
How does orthopedic treatment differ from standard wound care?
Orthopedic treatment addresses underlying structural and bone-related issues, combining surgical interventions, advanced therapies, infection control, and rehabilitation, whereas standard wound care focuses primarily on surface-level healing.