Understanding Infected Wounds in Orthopedic Care
In the field of orthopedics, wounds play a critical role in the healing process, especially after surgery or traumatic injuries. However, when these wounds become infected, they can turn into serious medical concerns that delay recovery and threaten long-term function. An infected wound occurs when harmful bacteria or other pathogens enter the tissue, leading to inflammation and impaired healing. This is particularly concerning in orthopedic patients, since infections can spread to muscles, tendons, or even bones, complicating recovery. Symptoms such as redness, swelling, fever, pus, or increasing pain should never be ignored, as they often indicate infection. If left untreated, an infected wound can lead to conditions like osteomyelitis, which is a bone infection that can compromise mobility and require extensive treatment. Understanding the risks of wound infections highlights why orthopedic specialists play such an essential role in preventing complications and ensuring patients regain their health and mobility.
How Orthopedic Specialists Diagnose Infected Wounds
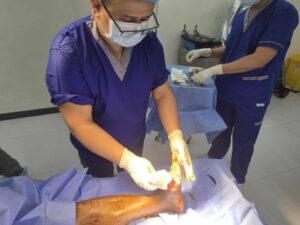
When a wound shows signs of infection, orthopedic specialists take a thorough and structured approach to diagnosis. The process begins with a detailed physical examination where the wound is carefully inspected for discharge, odor, and changes in skin color. Swelling and tenderness around the affected area are also assessed, as these may indicate deeper tissue involvement. Laboratory tests are often ordered, including blood work and wound swabs, to identify the specific bacteria causing the infection. Imaging techniques like X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans may be used to determine whether the infection has reached deeper tissues or bones, which is critical for forming an effective treatment plan. Early and precise diagnosis ensures that patients receive targeted care instead of generalized treatment, reducing the risk of prolonged healing or surgical complications. Without this level of thoroughness, infections could easily progress unnoticed, leading to more invasive interventions down the road. By using advanced diagnostic tools and medical expertise, orthopedic specialists provide patients with a clear path toward recovery.
Medical Approaches to Treating Infected Wounds
For many patients, the first line of orthopedic treatment for infected wounds involves medical therapies designed to stop infection and support healing. Antibiotics are commonly prescribed, with choices tailored to the type of bacteria found through cultures and lab results. In addition to systemic antibiotics, topical treatments such as antimicrobial dressings may be used to provide direct protection at the wound site. Pain management also plays a significant role in treatment, since infections often cause discomfort that can hinder movement and slow recovery. Anti-inflammatory medications may be given to reduce swelling and improve mobility around the injured area. Another essential approach is debridement, which involves removing dead or infected tissue so the wound can heal effectively. This step is crucial because it prevents bacteria from thriving in unhealthy tissue and creates a clean environment for healing. Combined, these medical approaches form the foundation of effective orthopedic wound care and give patients the best chance for recovery without extensive surgical involvement.
Surgical Interventions in Orthopedic Treatment for Infected Wounds
When infections persist or worsen despite medical therapies, surgical intervention may become necessary. Orthopedic surgeons perform specialized procedures designed to remove infected tissue and restore proper healing conditions. One of the most common techniques is irrigation and debridement, where the wound is thoroughly cleaned and unhealthy tissue is excised. In more severe cases, skin grafts or flap procedures may be required to close large wounds or replace damaged tissue with healthy coverage. Deep infections that reach muscles, tendons, or bones require even more careful intervention to prevent long-term complications like impaired mobility or bone damage. After surgery, orthopedic specialists monitor patients closely to ensure infections do not recur and healing progresses as expected. Post-surgical care often involves a combination of antibiotics, specialized dressings, and follow-up imaging to verify that the infection has been controlled. This proactive approach allows patients to regain mobility and avoid long-term complications while ensuring the infection is fully eradicated.
Innovative and Advanced Treatment Options
Modern orthopedic medicine continues to evolve, offering innovative therapies for infected wounds that go beyond traditional care. Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT), for instance, uses suction technology to remove excess fluid and bacteria while promoting blood flow and tissue repair. Bioengineered skin substitutes and regenerative medicine techniques provide additional tools for healing wounds that are resistant to conventional treatments. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is another advanced option, exposing patients to high oxygen levels in a pressurized environment to speed healing and fight infection. These therapies are especially valuable for patients with complex infections, chronic illnesses, or wounds that do not respond well to standard treatment methods. Orthopedic surgeons often integrate these modern approaches alongside medical and surgical treatments, tailoring care to each patient’s unique needs. This combination of science, technology, and medical expertise ensures that even the most difficult infections can be managed effectively. By embracing innovation, orthopedic care offers patients renewed hope and improved outcomes in their healing journey.
The Role of Rehabilitation and Long-Term Care
Healing from an infected wound does not stop once the infection has cleared; long-term rehabilitation is often necessary to restore full function. Physical therapy is a key component, helping patients rebuild strength, mobility, and flexibility in the affected area. Nutritional support is equally important, as diets rich in protein, vitamins, and minerals enhance the body’s ability to fight infection and repair tissue. Scar management may also be part of recovery, since infections can leave behind lasting marks that affect both function and appearance. Psychological support plays a vital role as well, since patients recovering from prolonged infections may struggle with anxiety or frustration. Orthopedic specialists emphasize a holistic approach that addresses both physical and emotional needs, ensuring patients return to daily life with confidence. Regular follow-up appointments allow doctors to monitor healing and adjust care as needed, preventing setbacks. This long-term focus reinforces the idea that recovery is not just about healing the wound but also about regaining overall health and quality of life.
Preventing Future Infections in Orthopedic Patients
Prevention is always better than treatment, and orthopedic specialists place strong emphasis on educating patients about infection prevention. Proper wound care at home is essential, including regular cleaning, correct dressing changes, and maintaining hygiene. Patients are encouraged to attend all follow-up visits so doctors can catch potential issues before they develop into serious infections. Lifestyle factors also play an important role, such as quitting smoking, managing diabetes, and maintaining a strong immune system through healthy living. Nutrition, hydration, and rest further support the body’s ability to resist infection and recover quickly from minor injuries. Orthopedic teams often provide personalized education for patients and caregivers, ensuring they understand how to care for wounds effectively. By adopting these preventive measures, patients reduce their risk of future complications and strengthen their overall recovery process. The combination of medical expertise and patient awareness creates a powerful defense against infections, ensuring better outcomes for anyone undergoing orthopedic care.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the most common cause of wound infections in orthopedic patients?
The most common cause is bacterial contamination, which may occur after surgery, injury, or improper wound care. Conditions like diabetes or weakened immunity can further increase the risk.
How do I know if my wound infection needs immediate orthopedic care?
If you notice spreading redness, severe pain, pus, fever, or worsening swelling, it’s important to seek orthopedic care right away. Delays can lead to serious complications, including bone infections.
Can an infected wound heal without antibiotics?
In most cases, antibiotics are necessary to control infection. While minor wounds may heal naturally, infected wounds almost always require medical treatment to prevent the spread of bacteria.
What are the risks of untreated infected wounds?
Untreated infections can spread deeper into tissues and bones, leading to osteomyelitis, abscesses, or even systemic infections. These complications can significantly delay recovery and may require surgery.
How long does recovery usually take after orthopedic wound treatment?
Recovery time varies depending on the severity of infection and treatment type. Minor infections may heal within weeks, while more complex cases involving surgery can take several months of care and rehabilitation.