What an Open Wound Doctor Does
An open wound doctor specializes in diagnosing and managing wounds that fail to heal properly on their own. These medical professionals go beyond the capabilities of general practitioners, offering focused expertise in wound assessment, infection control, and long-term treatment. Open wound doctors treat various types of wounds, including pressure ulcers, diabetic foot wounds, surgical site infections, venous leg ulcers, and traumatic injuries. Their role includes addressing both acute and chronic conditions that compromise skin integrity. They often work in hospital wound clinics, private wound care centers, outpatient surgical facilities, and home health services. Their approach combines a deep understanding of human physiology with advanced technology to help patients recover more effectively. With the rise in diabetes and vascular diseases, these specialists are becoming increasingly vital in healthcare.
When You Should See an Open Wound Doctor
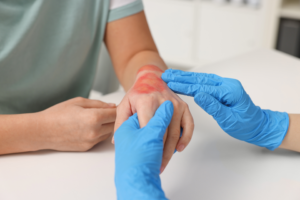
Delaying proper wound care can lead to severe health risks. If a wound shows no signs of healing within 10 to 14 days, or if it begins to worsen, a visit to an open wound doctor is advised. Common signs of trouble include redness spreading beyond the wound, pus or foul-smelling discharge, increasing pain, and swelling. Another critical indicator is fever, which may suggest systemic infection. Some people mistakenly believe they can treat complex wounds at home with over-the-counter ointments or homemade remedies. However, these methods often mask deeper issues and delay necessary medical intervention. Anyone with diabetes, poor circulation, or a compromised immune system should seek medical help at the first sign of a problem. Early intervention by an open wound doctor significantly improves healing outcomes and prevents complications.
Common Procedures Used by Open Wound Doctors
Open wound doctors use a range of clinical procedures based on the type, size, and severity of the wound. One common method is debridement, the removal of dead or infected tissue to promote healing. This can be done surgically, chemically, or with special dressings that dissolve necrotic tissue. Advanced dressings, such as hydrocolloid, alginate, and foam dressings, help maintain moisture balance and protect against bacteria. Another critical tool is negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT), which uses suction to remove fluids and promote tissue growth. These specialists also use culture swabs to detect infection and guide antibiotic therapy. Diagnostic tools like Doppler ultrasound or imaging may be employed to assess underlying conditions. Each step is designed to create an environment where the wound can heal efficiently and safely.
What to Expect During Your Appointment
A visit to an open wound doctor typically begins with a thorough assessment of the wound and a review of the patient’s medical history. This includes measuring the wound, checking for signs of infection, and evaluating any underlying conditions such as diabetes or vascular problems. Imaging studies or lab tests might be ordered to better understand the severity of the wound. After assessment, the doctor creates a treatment plan tailored to the patient’s needs. This plan could include regular debridement, dressing changes, medication, or referrals to other specialists. Open wound doctors also focus on educating the patient about home care techniques and signs of complications. Follow-up visits are often scheduled to monitor healing progress and adjust treatments as needed. This personalized approach helps ensure that every aspect of wound care is addressed.
How Open Wound Doctors Help Prevent Complications
One of the most important roles of an open wound doctor is preventing severe complications. Untreated or poorly managed wounds can lead to infections, cellulitis, abscesses, or even sepsis. In extreme cases, amputation becomes a risk. These doctors use advanced techniques and regular monitoring to stop complications before they occur. By identifying infection early and applying the appropriate treatment, they safeguard the patient’s health. They also work to reduce inflammation, improve circulation, and minimize scar tissue formation. Prevention extends beyond the wound itself to overall patient health, addressing conditions like high blood sugar and hypertension. This proactive management is essential for patients with chronic wounds, who often face long-term recovery challenges. By involving an open wound doctor early, patients dramatically lower their risk of serious health issues.
The Role of Patient Participation in Wound Healing
Patient involvement plays a vital role in successful wound recovery. Open wound doctors educate patients on the importance of following medical instructions, such as changing dressings on schedule and taking prescribed medications. Proper nutrition also supports healing, as the body requires protein, vitamins, and minerals to repair tissue. For individuals with diabetes, maintaining stable blood sugar is critical to avoid delays in healing. Physical activity and pressure management can also influence recovery, especially for pressure ulcers. Patients are encouraged to avoid smoking, which restricts blood flow and hinders the healing process. Emotional well-being matters too; stress and depression can negatively impact immune function. Open wound doctors provide not only treatment but also guidance and encouragement, ensuring that patients play an active role in their own healing process.
Choosing the Right Open Wound Doctor
Finding the right open wound doctor is a crucial step in recovery. Patients should look for board certification, relevant experience, and familiarity with advanced wound care methods. It’s important to ask questions about treatment options, expected outcomes, and the technologies available at the clinic. Some doctors offer more personalized approaches, including tailored treatment plans and access to specialized therapies. Checking patient reviews and referrals can provide insight into a doctor’s reputation. Insurance compatibility and clinic location are also practical considerations. The doctor’s willingness to coordinate with other healthcare providers is another key factor, especially if the patient has multiple conditions. A good open wound doctor makes the patient feel informed, respected, and supported throughout their healing journey.
How Open Wound Doctors Support Long-Term Recovery
The work of an open wound doctor doesn’t end once the wound closes. They continue to monitor the site for signs of recurrence or infection and provide recommendations for long-term care. Preventive strategies may include physical therapy, lifestyle changes, and routine checkups. In some cases, patients receive training on how to manage wounds at home, especially for those with recurring issues. Education about foot care for diabetic patients is common, as is skin care guidance for those prone to pressure sores. Emotional support is also important, particularly for those who’ve endured long healing periods. Open wound doctors often collaborate with counselors, dietitians, and other professionals to offer a comprehensive care plan. This extended support helps patients maintain a healthy recovery and avoid future complications.
Frequently Asked Questions About Open Wound Doctors
1. What’s the difference between a wound care nurse and an open wound doctor?
An open wound doctor is a medical doctor with specialized training in wound treatment, whereas a wound care nurse provides daily wound management and support under the doctor’s guidance.
2. How long does it take for a chronic wound to heal under specialist care?
Healing time varies, but with the right treatment, many chronic wounds show improvement within weeks. Full healing may take several months, depending on the severity and underlying conditions.
3. Do I need a referral to see an open wound doctor?
Some clinics require a referral from a primary care physician, but others allow direct appointments. It depends on the clinic’s policy and your insurance requirements.
4. Can they treat wounds at home or only in clinics?
Some open wound doctors offer home visits or work with home health agencies. However, advanced procedures typically require clinical settings.
5. What happens if an infection spreads before seeing a specialist?
A spreading infection can become life-threatening. Emergency care may be necessary, and a specialist will need to act quickly to prevent further complications.