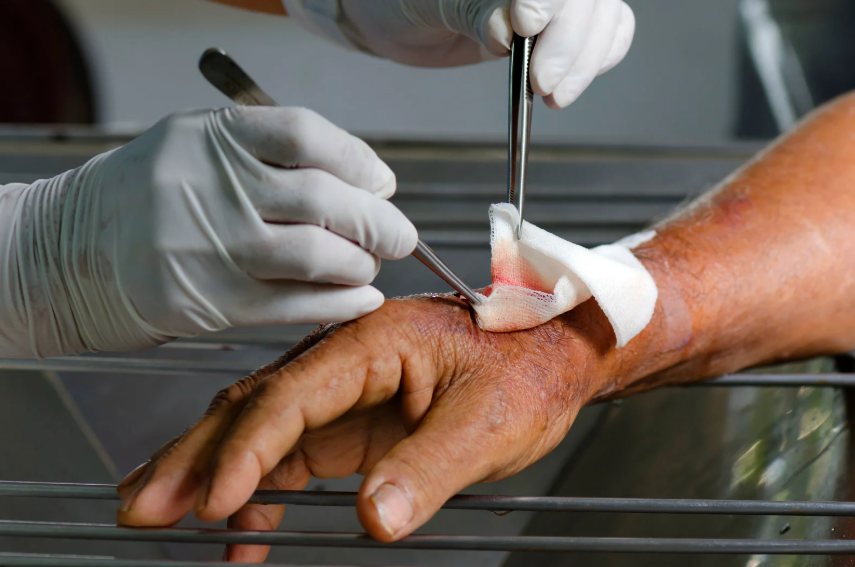
An infected wound can quickly escalate into a severe health issue if not treated promptly. Wound infections occur when bacteria enter a cut, burn, or surgical incision, leading to inflammation, pus formation, and tissue damage. When left untreated, these infections can spread to deeper tissues, bones, and joints, requiring orthopedic treatment for infected wounds to prevent long-term complications. Recognizing the key warning signs of an infected wound is crucial to seeking the right medical intervention in time.
Understanding Infected Wounds
An infected wound is a break in the skin that becomes contaminated by harmful bacteria, leading to inflammation and delayed healing. These infections are particularly concerning when they involve deeper structures like muscles, tendons, or bones, requiring specialized orthopedic treatment for infected wounds. Some common causes of wound infections include:
- Trauma-related injuries, such as deep cuts or puncture wounds
- Post-surgical complications from orthopedic procedures
- Chronic wounds in individuals with diabetes or poor circulation
- Unsterilized or improperly treated wounds
If not treated in time, wound infections can lead to abscess formation, cellulitis, or even life-threatening sepsis, making orthopedic treatment for infected wounds essential.
Key Warning Signs of an Infected Wound
Timely identification of infection is key to preventing complications. Here are the most common warning signs that indicate the need for orthopedic treatment for infected wounds:
Persistent Pain and Swelling
While some pain and swelling are expected during the healing process, excessive or worsening pain might indicate an infection. If the pain increases instead of subsiding, the infection could be spreading deeper, requiring orthopedic treatment for infected wounds to prevent further complications.
Redness and Warmth
Infected wounds often exhibit increasing redness, which may expand outward in a circular pattern. If the surrounding skin feels unusually warm to the touch, it is a strong indication that the body is fighting an infection. Orthopedic treatment for infected wounds is necessary if redness continues to spread beyond the immediate wound area.
Pus or Unusual Drainage
Healthy wounds typically produce clear or slightly yellowish fluid, but thick, foul-smelling pus that is green, brown, or yellow is a sign of infection. In such cases, orthopedic treatment for infected wounds is needed to drain the infection and prevent its progression to deeper tissues or the bloodstream.
Fever and Chills
A systemic infection can cause fever, chills, and sweating. If an individual experiences flu-like symptoms alongside a worsening wound, it is a sign that the infection is spreading beyond the localized area. Orthopedic treatment for infected wounds is crucial at this stage to prevent sepsis or osteomyelitis.
Delayed Healing
Wounds that take longer than expected to heal may be infected. If a wound remains open, swollen, or shows no improvement despite proper care, it may require orthopedic treatment for infected wounds to eliminate the underlying infection.
Numbness or Loss of Sensation
An infected wound affecting nerves can result in numbness, tingling, or a complete loss of sensation. This is a serious warning sign, particularly for individuals with diabetes or neuropathy, and necessitates immediate orthopedic treatment for infected wounds to prevent permanent nerve damage.
When to Seek Orthopedic Treatment for an Infected Wound
Recognizing when a wound requires medical intervention is critical. The following scenarios indicate the need for orthopedic treatment for infected wounds:
- Home Treatments Fail: If basic wound care methods such as cleaning, dressing, and using topical antibiotics do not improve the condition within a few days.
- Deep Tissue or Bone Involvement: When an infection extends into muscles or bones (osteomyelitis), specialized orthopedic care is essential.
- Post-Surgical Wound Infections: After orthopedic surgery, any signs of infection must be addressed immediately to prevent implant rejection or joint complications.
- Diabetes or Poor Circulation: Individuals with diabetes or vascular diseases have a higher risk of developing chronic, non-healing infected wounds, requiring expert orthopedic treatment for infected wounds.
Orthopedic Treatment Options for Infected Wounds
The treatment approach depends on the severity and depth of the infection. Common orthopedic treatment for infected wounds includes:
Antibiotic Therapy
Oral or intravenous antibiotics are prescribed to control the bacterial infection. In cases of severe infection, a prolonged course of IV antibiotics may be required as part of orthopedic treatment for infected wounds.
Debridement Procedures
Debridement involves removing dead or infected tissue to promote healing. This surgical intervention is crucial in preventing further bacterial spread and is a key part of orthopedic treatment for infected wounds.
Surgical Intervention
In cases where the infection has reached bones or joints, orthopedic surgery may be necessary to remove infected bone tissue and prevent further complications. Procedures like bone grafting or hardware removal might be required as part of orthopedic treatment for infected wounds.
Wound Care Management
Specialized dressings, negative pressure wound therapy, and routine monitoring are essential to ensuring proper healing. Orthopedic treatment for infected wounds includes personalized wound management plans to facilitate recovery.
Preventing Wound Infections: Best Practices
Preventive measures play a crucial role in avoiding the need for orthopedic treatment for infected wounds. Follow these steps:
- Keep wounds clean and dry. Use antiseptic solutions and sterile bandages.
- Monitor wounds daily. Look for any signs of infection such as redness, swelling, or unusual discharge.
- Control underlying conditions. Diabetes and poor circulation increase infection risks, so managing these conditions can reduce complications.
- Follow post-surgical care instructions. Patients recovering from orthopedic procedures should adhere to their doctor’s wound care recommendations.
- Seek medical attention early. The earlier an infection is detected, the more effective orthopedic treatment for infected wounds will be in preventing serious health risks.
Takeaway
Ignoring the warning signs of an infected wound can lead to severe complications, including deep tissue infections and bone damage. Understanding the symptoms and seeking timely orthopedic treatment for infected wounds can prevent long-term health issues. If you or a loved one experiences persistent pain, swelling, redness, unusual drainage, or fever, it is essential to consult an orthopedic specialist immediately. Early intervention can make a significant difference in recovery and overall well-being.