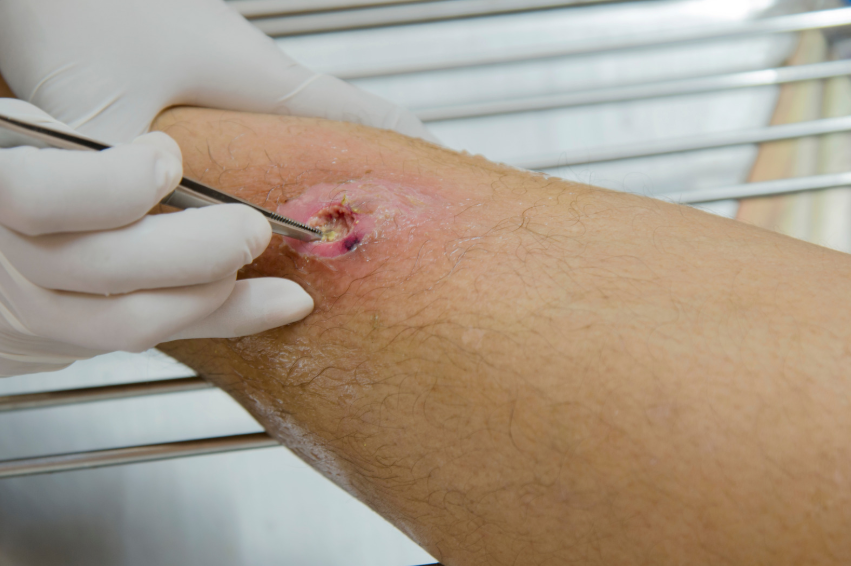
Orthopedic treatment for infected wounds is a critical aspect of care in both trauma and surgical settings. Proper infection control is essential to ensure optimal recovery and prevent complications such as osteomyelitis and sepsis. Infection control in orthopedic surgery and trauma is an ongoing concern, as infected wounds can significantly prolong recovery time, increase healthcare costs, and negatively impact patient health. Effective infection prevention strategies, both pre- and post-surgery, are essential for reducing the risks associated with orthopedic wounds. This article will explore orthopedic approaches to infection control, focusing on traumatic and surgical wounds.
Understanding Orthopedic Wounds
Orthopedic treatment for infected wounds begins with understanding the types of wounds encountered in orthopedic care. Traumatic wounds result from accidents, falls, or other external forces, while surgical wounds are created during orthopedic procedures such as fracture repairs or joint replacements. Both types of wounds are vulnerable to infection, but the risk factors and treatment protocols may vary. Orthopedic surgeons must assess each wound type to determine the most effective infection control strategy. Traumatic orthopedic wounds often involve external contaminants and may be more difficult to manage, whereas surgical wounds may be controlled more easily with prophylactic antibiotics and sterile techniques.
Common Infections in Orthopedic Wounds
Infections in orthopedic wounds can range from mild to severe, and orthopedic treatment for infected wounds depends on the type of infection. Osteomyelitis, a bone infection, and septic arthritis, which affects the joints, are two common types of infections that orthopedic surgeons must address. Soft tissue infections can also occur in traumatic wounds, particularly when foreign materials or dirt are introduced into the wound site. Effective management of orthopedic infections involves early detection and prompt treatment. Prolonged untreated infections in traumatic and surgical wounds can lead to chronic issues that require more intensive orthopedic treatment for infected wounds, including surgery or long-term antibiotic therapy.
Orthopedic Infection Control Strategies
Orthopedic treatment for infected wounds begins with comprehensive infection control strategies. Pre-operative infection control is vital in reducing the risk of infection in surgical wounds. Surgeons take measures such as using sterile techniques, administering prophylactic antibiotics, and ensuring the surgical area is clean and properly prepared. Intraoperative infection control involves maintaining a sterile environment, using antiseptics to cleanse the surgical site, and minimizing tissue handling to avoid contamination. After surgery, post-operative care is just as critical in preventing infection. Orthopedic surgeons recommend appropriate dressing changes, wound cleaning, and regular monitoring for signs of infection to ensure timely intervention if infection develops.
Role of Antibiotics in Orthopedic Infection Control
Antibiotics play a central role in orthopedic treatment for infected wounds. Prophylactic antibiotics are commonly administered before, during, and after orthopedic surgeries to minimize the risk of infection. The choice of antibiotic depends on the type of surgery and the patient’s health history. Antibiotics help prevent infection in surgical wounds and are also used to treat active infections. Proper antibiotic stewardship is crucial to prevent antibiotic resistance and ensure the most effective treatment. Overuse or misuse of antibiotics in orthopedic care can lead to complications such as resistant bacterial strains, making infection control more challenging. Orthopedic specialists must balance the use of antibiotics with other infection prevention methods to ensure optimal results.
Emerging Techniques and Technologies in Infection Prevention
The field of orthopedic treatment for infected wounds is evolving with the development of new technologies and techniques aimed at improving infection control. Antimicrobial coatings on surgical implants and wound dressings can reduce the risk of bacterial colonization and infection. Negative pressure wound therapy, which uses a vacuum to promote healing and reduce infection risk, has been increasingly used in managing complex orthopedic wounds. Additionally, robotic surgery offers enhanced precision and may reduce the risk of infection by minimizing human error and tissue damage. These advancements in orthopedic technology contribute to more effective infection control strategies, ultimately improving patient outcomes and reducing the need for prolonged orthopedic treatment for infected wounds.
Challenges in Orthopedic Infection Control
Despite advancements, orthopedic treatment for infected wounds remains challenging, particularly when infections involve deep tissue or bone. Bone and joint infections require a more aggressive approach, often including surgical debridement, long-term antibiotic therapy, and sometimes the removal of hardware. These infections are more complex due to the difficulty of antibiotics penetrating bone tissue and the risk of persistent infection even after treatment. Orthopedic specialists must also consider patient-specific factors, such as diabetes, smoking, and immunocompromised conditions, which increase the risk of infection. A multidisciplinary approach involving orthopedic surgeons, infectious disease experts, and wound care specialists is essential in managing these complex cases of orthopedic infection.
Patient Education for Infection Prevention
Patient education plays a vital role in orthopedic treatment for infected wounds, particularly after surgery or traumatic injury. Patients must be informed about the importance of proper wound care at home to reduce the risk of infection. This includes following instructions on dressing changes, monitoring for signs of infection, and maintaining cleanliness around the wound site. Patients should be aware of the symptoms of infection, such as redness, swelling, warmth, and fever, and seek medical attention promptly if these occur. Educating patients about the proper management of orthopedic wounds can reduce the need for additional treatments and minimize the risk of infection-related complications.
Takeaway
Orthopedic treatment for infected wounds requires a multi-faceted approach that includes preoperative planning, meticulous surgical techniques, antibiotic use, and post-operative care. Effective infection control is crucial for promoting healing and preventing long-term complications such as chronic infections or the need for repeated surgeries. With advancements in technology and a focus on patient education, orthopedic care continues to improve, ensuring better outcomes for patients dealing with traumatic and surgical wounds. By combining traditional methods with modern innovations, orthopedic specialists can effectively manage infected wounds and provide patients with the best chance for recovery.